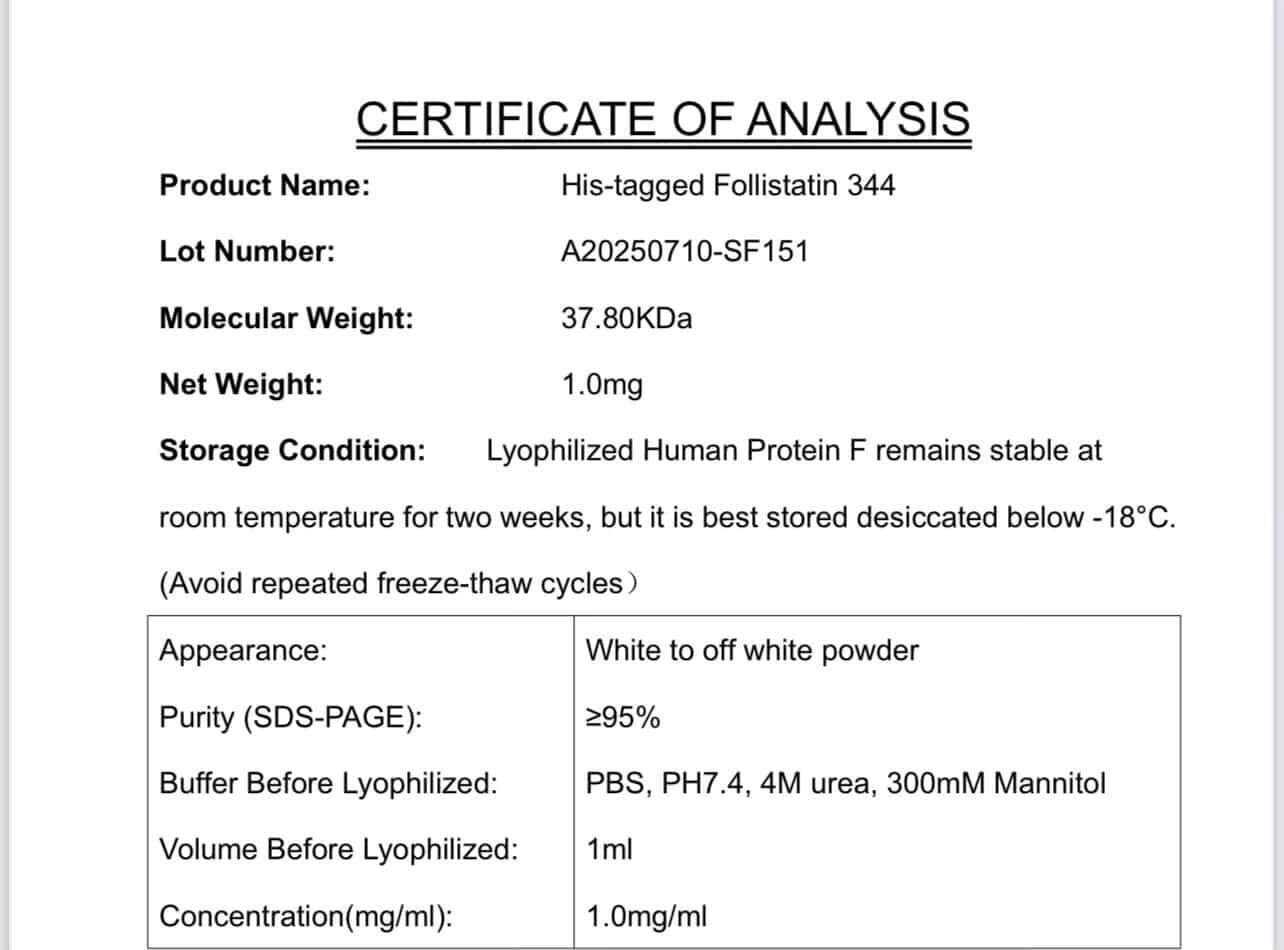
Follistatin 344 1mg
$170.00
You save
- Physical profile: Lyophilized powder
- This product is sold as a research chemical and not for human or animal consumption. For laboratory use by qualified professionals.
Availability: 38 in stock (can be backordered)
Availability: Ships today if ordered and paid by 12 PM EST. (Except Saturdays & Sundays)
Product Usage
Follistatin 344 1mg IS INTENDED AS A RESEARCH CHEMICAL ONLY. This designation allows the use of research chemicals strictly for in vitro testing and laboratory experimentation only. All product information available on this website is for educational purposes only. Bodily introduction of any kind into humans or animals is strictly forbidden by law. This product should only be handled by licensed, qualified professionals. This product is not a drug, food, or cosmetic and may not be misbranded, misused or mislabled as a drug, food or cosmetic.
Follistatin-344 1mg is a lab-made version of a natural protein called Follistatin. It works by blocking the effects of myostatin, activin, and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). In animal studies, this has been shown to increase muscle growth (both by making muscles bigger and creating new muscle cells), reduce scar tissue, and lower certain types of inflammation. The body can also change Follistatin-344 into other forms of Follistatin.
What Is Follistatin 344 Peptides?
Follistatin (FST) 344 is a man-made version of a natural protein called follistatin, which is found in almost all tissues of higher animals. There are two forms of follistatin, created through a process called gene splicing. Its main job is to block proteins in the TGF-beta family, especially activin, myostatin, and follicle-stimulating hormone.Follistatin 344 Structure
Sequence:
MVRARHQPGG LCLLLLLLCQ FMEDRSAQAG NCWLRQAKNG RCQVLYKTEL SKEECCSTGR LSTSWTEEDV NDNTLFKWMI FNGGAPNCIP CKETCENVDC GPGKKCRMNK KNKPRCVCAP DCSNITWKGP VCGLDGKTYR NECALLKARC KEQPELEVQY QGRCKKTCRD VFCPGSSTCV VDQTNNAYCV TCNRICPEPA SSEQYLCGND GVTYSSACHL RKATCLLGRS IGLAYEGKCI KAKSCEDIQC TGGKKCLWDF KVGRGRCSLC DELCPDSKSD EPVCASDNAT YASECAMKEA ACSSGVLLEV KHSGSCNSIS EDTEEEEEDE DQDYSFPISS ILEW Molecular Weight:3780 g/mol PubChem CID:178101631 Synonyms:Activin-Binding Protein, FSH-Suppressing Protein, FSTFollistatin 344 Effects
Follistatin Research and Muscle Growth
Myostatin is a protein that stops muscle cells from growing and developing. Follistatin can block myostatin, which has led scientists to explore its potential for improving muscle growth and treating conditions like muscular dystrophy. In studies with mice, follistatin increased muscle mass by 10% in just eight weeks, even without special diets or exercise. Research in animals, including monkeys, shows that follistatin therapy increases muscle size and strength. It also reduces inflammation and scar tissue in conditions like Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), leading to stronger muscles. Interestingly, a single dose of follistatin through gene therapy has provided long-term muscle growth and strength for over two years in mice, regardless of their age. Follistatin works by stimulating the insulin/IGF-1 pathway, which helps muscles grow, and it also boosts insulin production, linking it closely to insulin signaling.Follistatin May Improve Survival in Breast Cancer
Studies show that follistatin is usually under-expressed in breast cancer but is over-expressed in some cases. When over-expressed, tumors grow faster but are less likely to spread. Follistatin has been linked to better survival rates and fewer cases of cancer spreading. In a mouse model of breast cancer, follistatin blocked the spread of cancer to the lungs, even though it didn’t stop tumor growth. It also plays a role in non-cancerous breast conditions, where it promotes local growth but reduces the chance of cancer spreading to other parts of the body.Follistatin Research and Cancer Treatment
Follistatin has been studied in various cancers, not just breast and liver cancer. It has been linked to better survival in breast cancer but worse outcomes in lung, ovarian, and stomach cancers. Understanding these differences could help develop treatments tailored to specific cancers. Follistatin may also help slow cancer spread and improve survival rates, potentially leading to cancer prevention strategies or vaccines.Follistatin Associated with Cell Proliferation
Follistatin has a unique effect: it promotes cell growth but limits the spread of cancer. For example, in the liver, follistatin helps liver cells grow by blocking activin. This explains why follistatin can increase tumor growth but reduce the spread of cancer. It seems that cells focus their energy on growing rather than spreading when follistatin is present.Follistatin Research and Liver Protection
Follistatin has been shown to protect the liver by slowing down the early stages of scarring (fibrosis). In rat studies, follistatin reduced liver scarring by 32% and decreased liver cell death by 87%. This protective effect could help prevent liver disease from progressing to cancer.Follistatin Provides Insight into Congenital Blindness
During early development, the optic nerve must fuse properly for normal vision. High levels of TGF-beta proteins, like BMP, can prevent this fusion and lead to blindness. Follistatin can block these proteins, helping the optic nerve fuse and reducing the risk of blindness. Research suggests that follistatin supplementation during pregnancy could support proper optic nerve development.Follistatin Research and Hair Growth
Studies in humans show that follistatin, especially when combined with other hair growth treatments, can significantly improve hair growth. In a small trial, participants saw a 20% increase in hair density and a 13% increase in thickness after a single injection. These results lasted for at least a year.Follistatin Research and Insulin Deficiency and Diabetes
In mice, follistatin has been shown to increase the number of insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, improving insulin levels and lowering blood sugar. This also reduced diabetes symptoms and doubled the mice’s lifespans by preventing complications. Researchers hope follistatin could help treat both type 1 and type 2 diabetes by improving the function of the remaining insulin-producing cells, offering a more natural way to regulate insulin levels and improve outcomes.The Future of Follistatin Research
Follistatin research covers many areas, including cancer, muscle problems, hair growth, and diabetes. It’s a growing field, with new studies and discoveries being made all the time. Follistatin has a lot of potential for developing treatments for various diseases and for helping scientists better understand how the human body works. Follistatin 344 has shown moderate side effects, works well when injected under the skin, but doesn’t work as well when taken orally in mice. However, the dosage used in mice cannot be directly applied to humans. Follistatin 344 sold by Peptide Sciences is only for educational and scientific research and is not meant for human use. It should only be purchased by licensed researchers.References
Lee S.J. & McPherron A.C. (2001) — “Regulation of myostatin activity and muscle growth.” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 98(16): 9306–9311. doi:10.1073/pnas- This foundational work showed that follistatin antagonizes myostatin and that inhibiting myostatin leads to increased muscle growth.
- Demonstrated that follistatin-overexpressing mice show improved muscle regeneration, less fibrosis, and enhanced recovery after muscle injury.
- This review outlines use of the FS-344 isoform delivered via AAV gene therapy, reporting increased muscle size and strength in animal models, with minimal off-target effects.
- Demonstrates long-term increases in muscle mass and strength after single administration of myostatin inhibitors including follistatin in animal models.
- Demonstrated that delivery of FS-344 via AAV vector significantly increased muscle size and strength in primates, without apparent pathology in key organs.
- Showed that overexpression of follistatin in sheep myoblasts increases proliferation, supporting a broader effect across mammals.
- Suggests that follistatin can promote muscle hypertrophy even when myostatin is absent, pointing to additional pathways of action.
- Indicates potential for follistatin to counteract age-related muscle degeneration beyond simple mass gains.
- Extends follistatin research beyond rodents/primates — showing efficacy in large mammals, relevant for translational potential.
- Provides a broad overview of follistatin’s therapeutic potential and the science behind FS-344 research.
Protocol
Clinical Research
Related products
- Sale!
Out of stock
-
-
-