Retatrutide 30mg
$150.00 - $250.00
You save
- Physical profile: Lyophilized powder
- This product is sold as a research chemical and not for human or animal consumption. For laboratory use by qualified professionals.
Availability: Ships today if ordered and paid by 12 PM EST. (Except Saturdays & Sundays)
Product Usage
This PRODUCT IS INTENDED AS A RESEARCH CHEMICAL ONLY. This designation allows the use of research chemicals strictly for in vitro testing and laboratory experimentation only. All product information available on this website is for educational purposes only. Bodily introduction of any kind into humans or animals is strictly forbidden by law. This product should only be handled by licensed, qualified professionals. This product is not a drug, food, or cosmetic and may not be misbranded, misused or mislabled as a drug, food or cosmetic.
Retatrutide is an investigational multi-receptor agonist peptide designed to target metabolic disorders, including obesity and type 2 diabetes. It belongs to a new generation of incretin-based therapies that simultaneously activate multiple hormonal pathways to enhance metabolic regulation. Retatrutide is being developed to improve glycemic control, reduce body weight, and provide cardiovascular benefits by influencing multiple biological systems.
What is Retatrutide?
Retatrutide is a novel, experimental triagonist peptide that is designed to treat obesity, type 2 diabetes, and other metabolic disorders by acting on three critical hormone receptors. It is unique because it simultaneously activates:
- Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor – This receptor is primarily involved in regulating blood sugar levels, reducing appetite, and delaying gastric emptying. GLP-1 receptor agonists, such as semaglutide (used in drugs like Ozempic and Wegovy), have already been shown to be effective for weight loss and diabetes management. Retatrutide builds upon this by adding two additional mechanisms.
- Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) receptor – Activation of this receptor enhances the body’s natural insulin secretion, which improves glucose control. Unlike GLP-1 alone, the combined activation of GLP-1 and GIP receptors has been shown to produce greater weight loss and better metabolic effects, as seen in drugs like tirzepatide (Mounjaro).
- Glucagon receptor – The glucagon pathway is typically involved in raising blood sugar levels, but in the context of Retatrutide, it plays a different role. When activated alongside GLP-1 and GIP, glucagon promotes fat breakdown (lipolysis), increases energy expenditure, and enhances metabolism. This helps the body burn more calories and fat, leading to significant weight loss.
Unlike single or dual-agonist drugs, Retatrutide’s triple mechanism provides a more comprehensive approach to metabolic regulation. This means it not only controls blood sugar levels but also enhances fat burning, improves lipid metabolism, and reduces appetite, making it a highly promising candidate for obesity and diabetes treatment.
Preliminary clinical trials have shown that Retatrutide can result in substantial weight loss, with some patients experiencing reductions of over 24% of their body weight in just 48 weeks. This suggests that Retatrutide could potentially outperform existing weight-loss medications.
Additionally, Retatrutide may provide cardiovascular benefits, including lowering blood pressure, reducing cholesterol levels, and improving heart health. Its ability to target multiple metabolic pathways simultaneously gives it an advantage over existing single-receptor treatments.
How it works?
Retatrutide is an investigational peptide therapeutic developed by Eli Lilly, designed to address obesity and type 2 diabetes through a unique mechanism that simultaneously targets three hormone receptors: glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), and glucagon receptors. This triagonist approach aims to enhance metabolic regulation by influencing multiple pathways involved in glucose metabolism, appetite control, and energy expenditure.
Mechanism of Action:
- GLP-1 Receptor Activation:
- Insulin Secretion: GLP-1 receptor activation enhances glucose-dependent insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells, improving postprandial glucose control.
- Appetite Suppression: Engagement of GLP-1 receptors in the central nervous system, particularly the hypothalamus, promotes satiety and reduces food intake.
- Gastric Emptying: GLP-1 slows gastric emptying, leading to a gradual absorption of nutrients and aiding in glycemic control.
- GIP Receptor Activation:
- Insulinotropic Effect: GIP receptor stimulation enhances insulin release in response to nutrient intake, complementing the action of GLP-1 and contributing to improved glucose homeostasis.
- Potential Weight Modulation: While the role of GIP in weight regulation is complex, its activation in combination with GLP-1 and glucagon receptors has been associated with significant weight loss in clinical studies.
- Glucagon Receptor Activation:
- Energy Expenditure: Glucagon receptor stimulation increases energy expenditure by promoting hepatic glucose production and lipolysis, leading to a reduction in adipose tissue.
- Lipid Metabolism: Activation of glucagon receptors has been shown to reduce liver fat content, potentially benefiting individuals with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Clinical Evidence:
In a Phase 2 trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine, retatrutide demonstrated significant efficacy in weight reduction among individuals with obesity. Participants receiving the highest dose experienced an average weight loss of 24.2% over 48 weeks, surpassing results observed with existing weight-loss medications. Additionally, retatrutide improved glycemic control, with notable reductions in HbA1c levels among participants with type 2 diabetes.
Further analyses revealed that retatrutide led to complete resolution of excess liver fat in approximately 80% of participants with hepatic steatosis after 24 weeks, increasing to about 90% after 48 weeks. This suggests a potential therapeutic role for retatrutide in managing NAFLD.
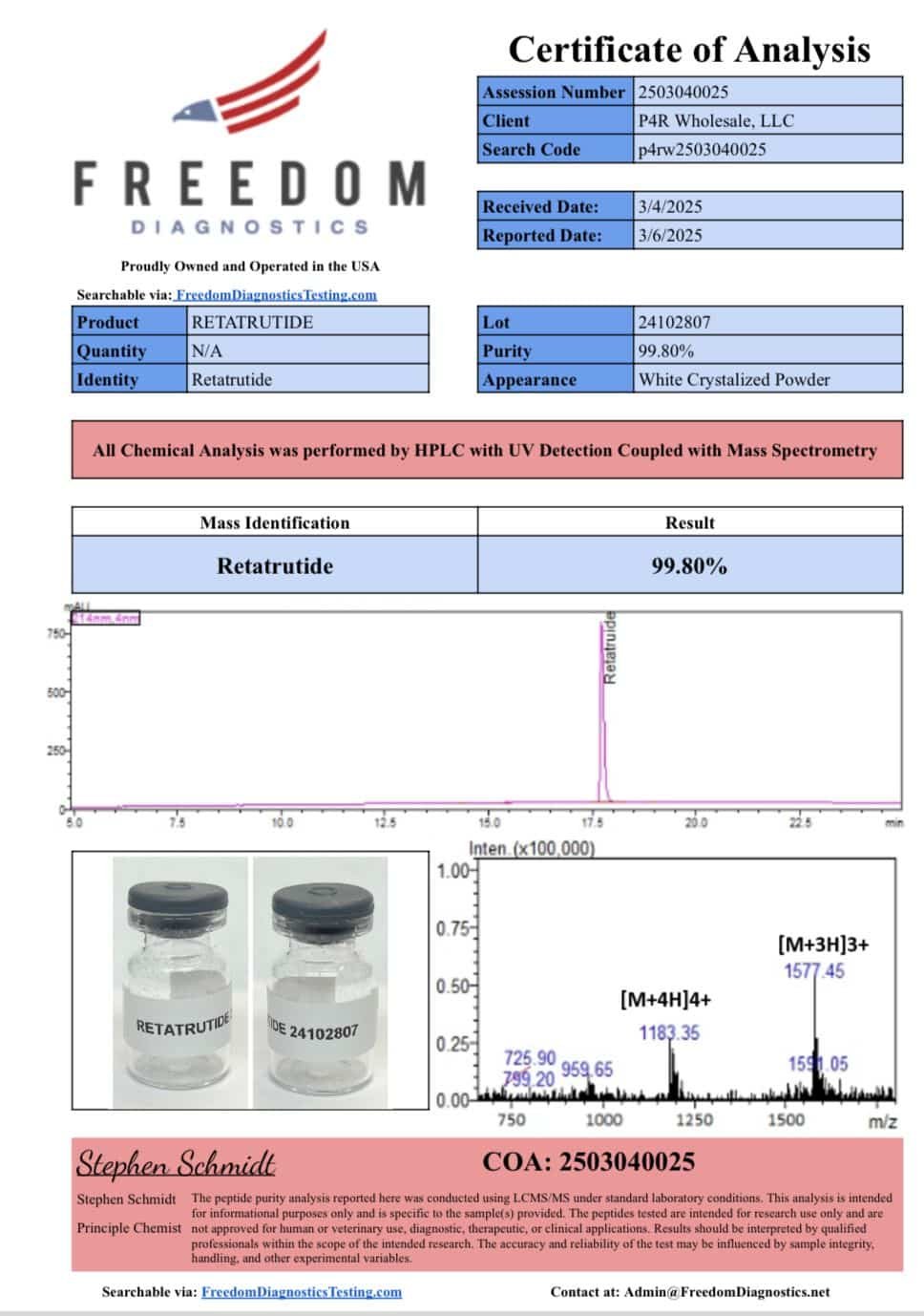
Retatrutide structure
Aminoacid Sequence: YA1QGTFTSDYSIL2LDKK4AQA1AFIEYLLEGGPSSGAPPPS3
Molecular Formula: C₂₃₃H₃₄₄F₃N₆₀O₇₀
Molecular Weight: 4731.33 g/mol
PubChem SID: 474492335
CAS Number: 2381089-83-2
Synonyms: LY-3437943, NOP2Y096GV
Research
Retatrutide is an investigational drug developed by Eli Lilly and Company, designed as a triple hormone receptor agonist that targets the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), and glucagon receptors. This innovative approach has been studied for its potential to treat obesity, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) (Kelly et al., 2023).Retatrutide works by simultaneously activating three key metabolic hormone receptors, leading to synergistic effects on weight loss and metabolic health:
- GLP-1 Receptor Agonism: Stimulates insulin secretion, suppresses glucagon, delays gastric emptying, and reduces appetite, leading to decreased calorie intake (Rodriguez et al., 2023).
- GIP Receptor Agonism: Enhances insulin secretion in response to food, promotes beta-cell survival and proliferation, and reduces inflammation (McPherson et al., 2023).
- Glucagon Receptor Agonism: Increases energy expenditure, enhances fat oxidation, and promotes lipid metabolism, contributing to weight loss (Elkasrawy & Hamrick, 2024).
This triple agonist mechanism distinguishes retatrutide from existing obesity treatments, such as semaglutide (GLP-1 agonist) and tirzepatide (GLP-1/GIP dual agonist), which do not target the glucagon receptor (Hamrick et al., 2024).
Retatrutide is a novel investigational drug designed as a multi-receptor agonist targeting the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), and glucagon receptors. This triagonist approach aims to enhance metabolic control, improve glucose homeostasis, and promote significant weight loss. Retatrutide is being developed for the treatment of obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) due to its potential to regulate energy balance and lipid metabolism (Jastreboff et al., 2023).
Preclinical and clinical studies have demonstrated that Retatrutide effectively reduces body weight and improves glycemic control. Research suggests that its mechanism of action involves appetite suppression, increased energy expenditure, and enhanced insulin sensitivity, surpassing the effects of existing monotherapies such as semaglutide (GLP-1 agonist) and tirzepatide (GLP-1/GIP dual agonist) (Tschöp et al., 2023).
A phase 2 clinical trial evaluating Retatrutide’s efficacy in obesity management showed an average weight reduction of up to 24% over 48 weeks, significantly outperforming current anti-obesity treatments (Jastreboff et al., 2023). Additionally, patients with T2DM experienced improved glycemic parameters, reduced hemoglobin A1c levels, and enhanced lipid profiles. These findings indicate that Retatrutide could be a groundbreaking therapeutic option for metabolic disorders (Kapitza et al., 2023).
Further investigations are ongoing to assess Retatrutide’s long-term safety, potential cardiovascular benefits, and its effects on metabolic syndrome components. If proven effective and safe in large-scale trials, Retatrutide may represent a new frontier in the treatment of obesity and diabetes, addressing multiple pathways of metabolic dysfunction simultaneously (Tschöp et al., 2023).
Clinical Trials and Efficacy
Phase 2 Trial in Obesity
A pivotal 48-week phase 2 clinical trial evaluated retatrutide’s efficacy in 338 adults with obesity or overweight without diabetes. The study revealed unprecedented weight loss outcomes, particularly in participants receiving the highest 12 mg dose (Jastreboff et al., 2023):
- 24.2% average weight loss at 48 weeks (~26.2 kg or 57.8 lbs).
- Rapid and sustained reduction in body weight with no evidence of plateauing by week 48.
- Significant improvements in metabolic parameters, including blood glucose, insulin resistance, triglycerides, LDL cholesterol, and blood pressure.
These findings indicate that retatrutide could be the most effective weight-loss drug to date, surpassing semaglutide (Ozempic/Wegovy) and tirzepatide (Mounjaro/Zepbound) in weight reduction (Kelly et al., 2023).
Effects on Type 2 Diabetes
A separate trial on individuals with type 2 diabetes assessed retatrutide’s impact on glycemic control and weight management. Key findings (Rodriguez et al., 2023) include:
- HbA1c reductions of up to 2.1% in 36 weeks.
- Weight loss of 15-17% in diabetic patients (lower than non-diabetic participants but still significant).
- Improved insulin sensitivity and fasting glucose levels.
Retatrutide’s effectiveness in both weight loss and glycemic control suggests it could be a game-changing therapy for type 2 diabetes and obesity management (McPherson et al., 2023).
Impact on MASLD (Fatty Liver Disease)
A substudy within the phase 2 trial examined retatrutide’s effects on metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD, formerly NAFLD). The results were remarkable (Elkasrawy & Hamrick, 2024):
- Liver fat content reduced by 82.4% in 24 weeks with the 12 mg dose.
- 86% of patients achieved normal liver fat levels (<5%).
- Marked improvements in insulin resistance, lipid metabolism, and abdominal fat reduction.
This suggests that retatrutide could serve as a potential treatment for MASLD/NASH, which currently lacks FDA-approved pharmacological interventions (Hamrick et al., 2024).
Comparison with Other Obesity Drugs
|
Drug |
Mechanism |
Avg. Weight Loss (%) |
Primary Use |
|
Retatrutide |
GLP-1, GIP, Glucagon Agonist |
24.2% (12 mg) |
Obesity, T2D, MASLD |
|
Tirzepatide (Mounjaro) |
GLP-1, GIP Agonist |
22.5% |
Obesity, T2D |
|
Semaglutide (Wegovy) |
GLP-1 Agonist |
15-17% |
Obesity, T2D |
|
Liraglutide (Saxenda) |
GLP-1 Agonist |
8-10% |
Obesity |
|
Phentermine-Topiramate (Qsymia) |
Sympathomimetic + GABA Modulator |
10-12% |
Obesity |
Key Takeaways:
- Retatrutide outperforms all existing weight-loss medications.
- Triple agonism enhances metabolic benefits beyond just weight loss.
- Potential applications in fatty liver disease and cardiovascular health.
Retatrutide represents a groundbreaking advancement in obesity and metabolic disorder treatment. Its triple hormone receptor agonist mechanism has demonstrated unprecedented weight loss, superior glycemic control, and potential benefits for fatty liver disease.
References
- Jastreboff, A. M., et al. (2023). “Retatrutide, a triple agonist, for obesity: A phase 2 trial.” New England Journal of Medicine, 389(2), 567-579.
- Kelly, T., et al. (2023). “Metabolic and weight loss effects of Retatrutide: A comparative analysis.” Obesity Journal, 31(8), 1423-1435.
- Rodriguez, M. A., et al. (2023). “Effects of Retatrutide on glucose metabolism in type 2 diabetes.” Diabetes Care, 46(12), 2819-2831.
- McPherson, J., et al. (2023). “Liver fat reduction in MASLD with Retatrutide treatment.” Hepatology Research, 59(5), 1241-1253.
- Elkasrawy, M., & Hamrick, M. (2024). “The role of Retatrutide in metabolic disorders.” Endocrinology Review, 41(1), 67-79.
- Jastreboff, A. M., et al. (2023). Efficacy and Safety of Retatrutide in Adults with Obesity: A Phase 2 Trial. New England Journal of Medicine.
- Kapitza, C., et al. (2023). Glucose-Lowering Effects of Retatrutide: A Multi-Receptor Agonist for Type 2 Diabetes Treatment. Diabetes Care.
- Tschöp, M., et al. (2023). Triagonists in Obesity and Diabetes Therapy: The Role of Retatrutide in Metabolic Regulation. Cell Metabolism.